A Deep Dive into the HEK293 Cell Line Family
Source: PricellaPublished: 2024-11-12
Origin of HEK293 Cells
The history of HEK293 cells dates back to 1973 when Dr. Alex Van Der Eb and Dr. Frank Graham at Leiden University in the Netherlands cultured these cells while studying human adenovirus. The number in the cell's name refers to the 293rd experiment in which the original cell clone was obtained. The cells were transfected with adenovirus type 5 (Ad5 DNA), which, due to the presence of the Ad5 E1A/B genes, altered the cell cycle, phenotype, and karyotype, resulting in immortalization. HEK293 cells are widely used in the production of adenoviral vectors, adeno-associated viral vectors, protein production, vaccine development, anti-cancer reagents, and cell biology research.
Characteristics and Uses of HEK293 Cell Lines
To date, there are several derived sublines of HEK293 cells, each with distinct characteristics and applications. Today, we will introduce the key features and uses of four major HEK293 subtypes: 293T, 293F, 293H, and 293S.
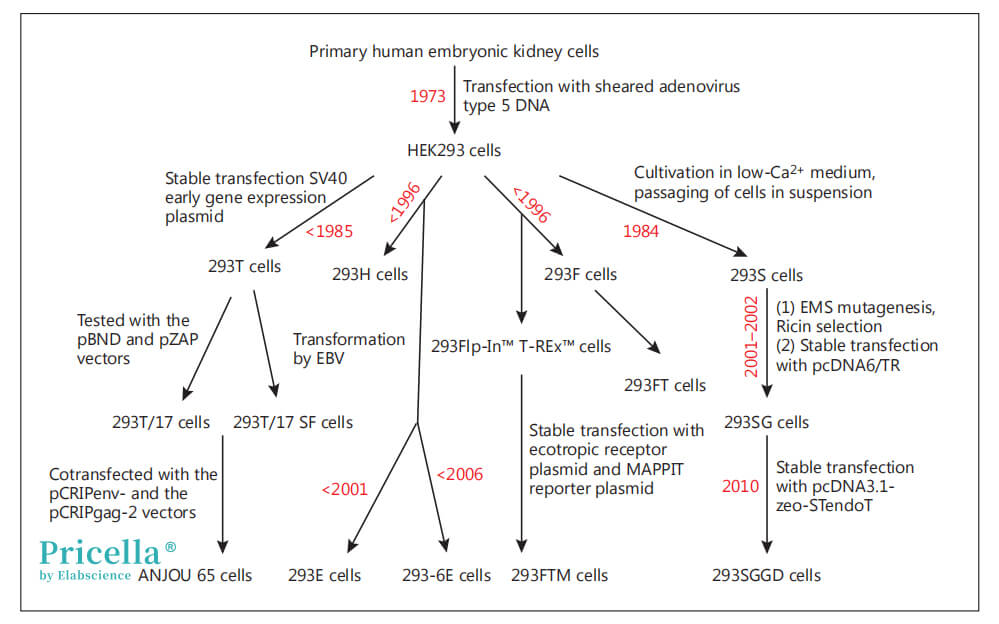
HEK293 Cell Line and Its Derivatives: A Schematic Overview
HEK293T
HEK293T is a subclone of the HEK293 cell line, modified to express the SV40 T antigen. The expressed SV40T antigen enables the amplification of foreign expression vectors, ultimately increasing the expression of target genes. It is commonly used for the packaging of lentiviruses, retroviruses, and adenoviruses.
HEK293H
HEK293H cells are derived from HEK293 cells expressing the E1A gene of adenovirus. These cells have strong adhesion properties and are commonly used in plaque assays and for recombinant protein expression and production. Insertion of the EBNA-1 gene into HEK293H cells results in the creation of 293E cells. These cells contain recombinant expression vectors with the EBV origin of replication (oriP), allowing replication within 293E cells and significantly enhancing protein expression. 293-6E cells are derived from HEK293H cells expressing a truncated EBNA1 gene, which allows for protein expression and viral vector production in serum-free culture systems.
HEK293F
HEK293F is a cell line derived from HEK293 cells that can grow rapidly in serum-free medium and is highly efficient for protein expression. When the pCMVSPORT6TAg.Neo plasmid is introduced into 293F cells, it creates 293FT cells, which are used for the production of lentiviral vectors and gene editing. The 293FTM cells are derived from Flp-In™ T-REx™ 293 cells that have been transfected with ecotropic reporter plasmids and MAPPIT (Mammalian Protein-Protein Interaction Trap) reporter plasmids, making them suitable for protein-protein interaction screening.
HEK293S
HEK293S cells are adapted through gradual cultivation to a suspension culture that can tolerate low Ca²⁺ conditions. These cells are often genetically modified using methanesulfonic acid mutagenesis and ricin toxin selection. When transfected with the pcDNA6/TR plasmid, they give rise to 293SG cells, which are commonly used for expressing homologous N-glycosylated proteins. This cell line also contains a tetracycline expression silencing gene, allowing for tetracycline-inducible protein expression studies. When transfected with the pcDNA3.1-zeo-STendoT plasmid, 293SG cells become 293SGGD cells, which are useful in glycosylation engineering research.
Applications of HEK293 Cells
HEK293 cells are widely used in various research fields, as summarized below:
Receptor Signaling: HEK293 cells can be used for the heterologous expression of ion channels and cell membrane receptors, commonly utilized to study G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling pathways related to diseases.
Cancer Research: Due to their tumorigenic properties, HEK293 cells are often employed in cancer research. They are suitable for testing and analyzing the effectiveness of cancer treatments.
Protein Production: HEK293 cells are capable of producing large quantities of recombinant proteins, making them ideal for vaccine development and the production of biotherapeutic proteins.
Gene Expression Studies: HEK293 cells are commonly used for transfection experiments to study gene or protein expression, aiding in research on gene function, protein function, and genetic mutations.
References
1. Hu J, Han J, Li H, et al. Human Embryonic Kidney 293 Cells: A Vehicle for Biopharmaceutical Manufacturing, Structural Biology, and Electrophysiology. Cells Tissues Organs. 2018;205(1):1-8. doi:10.1159/000485501
2. Stepanenko AA, Dmitrenko VV. HEK293 in cell biology and cancer research: phenotype, karyotype, tumorigenicity, and stress-induced genome-phenotype evolution. Gene. 2015;569(2):182-190. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2015.05.065
3. Lin YC, Boone M, Meuris L, et al. Genome dynamics of the human embryonic kidney 293 lineage in response to cell biology manipulations. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4767. Published 2014 Sep 3. doi:10.1038/ncomms5767
Prev: Uncovering the crucial science behind bFGF
Next: C2C12 Cell Cultivation Strategy and Differentiation Protocol - Pricella





