Does BEAS-2B Require Serum for Culture?
Source: PricellaPublished: 2025-01-02
Introduction to BEAS-2B
BEAS-2B (human normal lung epithelial cells) is an immortalized human bronchial epithelial cell line via SV40 large T antigen. It is widely used as an in vitro model for pulmonary epithelial cells in toxicological testing, respiratory injury, wound healing, and tumor transformation studies. Furthermore, it is an excellent host for transfection experiments.
Why Does BEAS-2B Exhibit Different Phenotypes?
While BEAS-2B cells typically display epithelial-like morphology, some researchers have reported fibroblast-like appearances (see Figure 1), deviating from the epithelial morphology shown in ATCC.
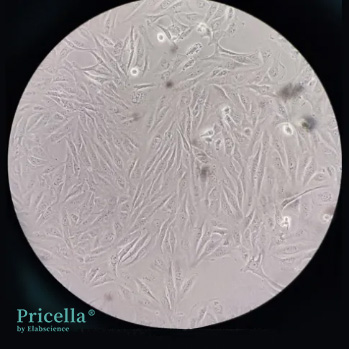
Figure 1: Morphology of BEAS-2B cultured by a customer (for reference only)
This variation is attributed to BEAS-2B's ability to undergo squamous differentiation in response to serum exposure. The morphology varies based on whether serum is included in the culture medium. BEAS-2B cells are commonly cultured under two conditions:
1. BEBM (Bronchial Epithelial Cell Growth Medium, serum-free)
2. DMEM + 10% Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS)
• In serum-free BEBM, BEAS-2B cells exhibit the characteristic polygonal morphology of respiratory epithelial cells.
•
In medium containing serum, cells appear spindle-shaped at low density and shorten at higher densities.
Important Notes:
• Passage density should not be too low, with a minimum of 60% confluence required.
• When using BEBM, the culture flasks must be pre-coated with a mixture dissolved in BEBM containing: 0.01 mg/mL fibronectin, 0.03 mg/mL type I bovine collagen, and 0.01 mg/mL bovine serum albumin.
• Serum affects cell adhesion, consequently influencing cell morphology.
• Changes in culture conditions significantly impact both cell morphology and functionality.
• Avoid arbitrary modifications to culture conditions.
The Impact of Serum on BEAS-2B Cells[1]
1)Gene Expression:
Whole-genome gene expression comparisons of BEAS-2B cultured with or without FBS revealed significant alterations in various biological pathways, including those related to carcinogenesis and energy metabolism.
2) Metabolic Activity:
• Real-time measurements of oxygen consumption and glycolysis indicated that FBS culture conditions increased overall glycolytic capacity by 1.4-fold and basal respiration by 1.9-fold.
• Oxygen consumption for ATP production rose by 2.0-fold, and maximum respiration increased by 2.8-fold compared to serum-free conditions.
3)Transcriptome Alterations:
• Transcriptomic changes induced by exposure to 1 μM sodium arsenite in FBS-cultured BEAS-2B cells revealed that 43% of sodium arsenite-regulated genes were also modulated by FBS.
4)Cytotoxicity Sensitivity:
BEAS-2B cells exposed to 5% FBS for 8 weeks were nearly five times more sensitive to sodium arsenite cytotoxicity compared to serum-free conditions.
5) Phenotypic Changes:
FBS-induced phenotypic changes in BEAS-2B suggest that the choice of culture conditions must be carefully considered when using BEAS-2B as a model for arsenic toxicity.
Reference
[1] Zhao F , Klimecki W T . Culture conditions profoundly impact phenotype in BEAS‐2B, a human pulmonary epithelial model[J]. Journal of Applied Toxicology Jat, 2015, 35(8):945-951.
Prev: How to Handle Floating SK-BR-3 Cells?
Next: Key Considerations for Culturing NK-92 and and NK-92MI Cells





